
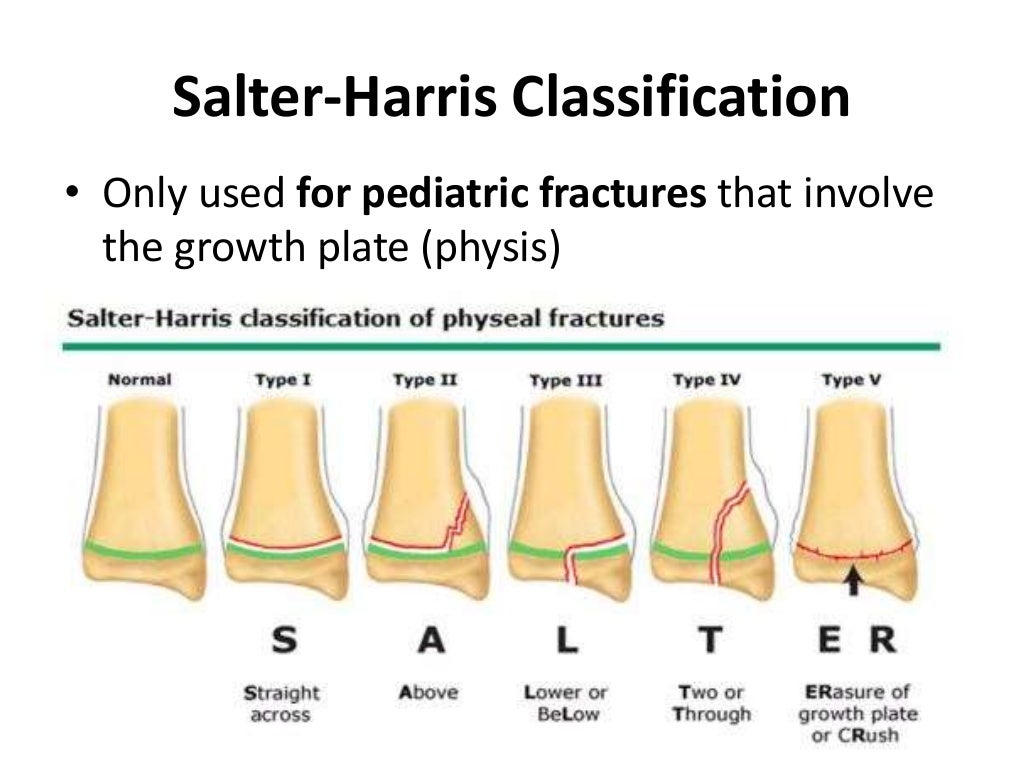
Girls are affected at a younger age (11 to 12 years) than boys (12 to 14 years). Males are more likely to be affected because they have an increased tendency to engage in high-risk activities. Of the five most common Salter-Harris fracture types, type II is the most common (75%) followed by types III (10%), IV (10%), type I (5%), and lastly, type V which is very rare 3). In general, upper extremity injuries are more common than lower-extremity injuries. Harris-Salter fractures are described exclusively in children and do not occur in the well-developed bones of adults. Salter-Harris fractures are common among children and comprise 15% to 30% of all bony injuries. Salter-Harris fracture classification system used to grade fractures according to the involvement of the growth plate (physis), metaphysis, and epiphysis is important as it has implications for both prognosis and treatment 2). Salter-Harris fracture also called growth plate fracture or physeal fracture, refers to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are therefore specifically applied to bone fractures in children 1). Salter Harris fracture long-term outcomes.(1993) Clinical orthopaedics and related research.
Compartment syndrome complicating tibial tubercle avulsion. Acute tibial tubercle avulsion fractures. Fracture of tibial tuberosity in an adult. Rodrigo Pires e Albuquerque, André Siqueira Campos, Gabriel Costa Serrão de Araújo, Vinícius Schott Gameiro. Anterior avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity in adolescents - Two case reports. Silva Júnior AT, Silva LJ, Silva Filho UC, Teixeira EM, Araújo HR, Moraes FB. (2008) Journal of children's orthopaedics. Tibial tuberosity fractures in adolescents. Frey S, Hosalkar H, Cameron DB, Heath A, David Horn B, Ganley TJ. type 3: displacement of the proximal base of the epiphysis with the fracture line extending into the joint.type 2: epiphysis is lifted cephalad and incompletely fractured.type 1: avulsion of the apophysis without injury to the tibial epiphysis.modifiers: A - nondisplaced and B - displaced.type V: avulsion of the periosteal sleeve.type IV: fracture through the entire physis.type III: fracture that traverses the primary and secondary ossification centers (most common type).type II: fracture between the primary and secondary ossification centers.type I: fracture of the secondary ossification center near the patella tendon insertion.

Modified Ogden classification (modification of Watson-Jones classification): The most commonly used is the modified Ogden classification. There are multiple classification systems with multiple modifiers.

compartment syndrome due to the recurrent branch of the anterior tibial artery injury.patella tendon or quadriceps tendon rupture.The typical patient is an adolescent male approaching skeletal maturity with well-developed quadriceps. These fractures have an incidence 0.4% to 2.7%, and males are affected more-so than females.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
